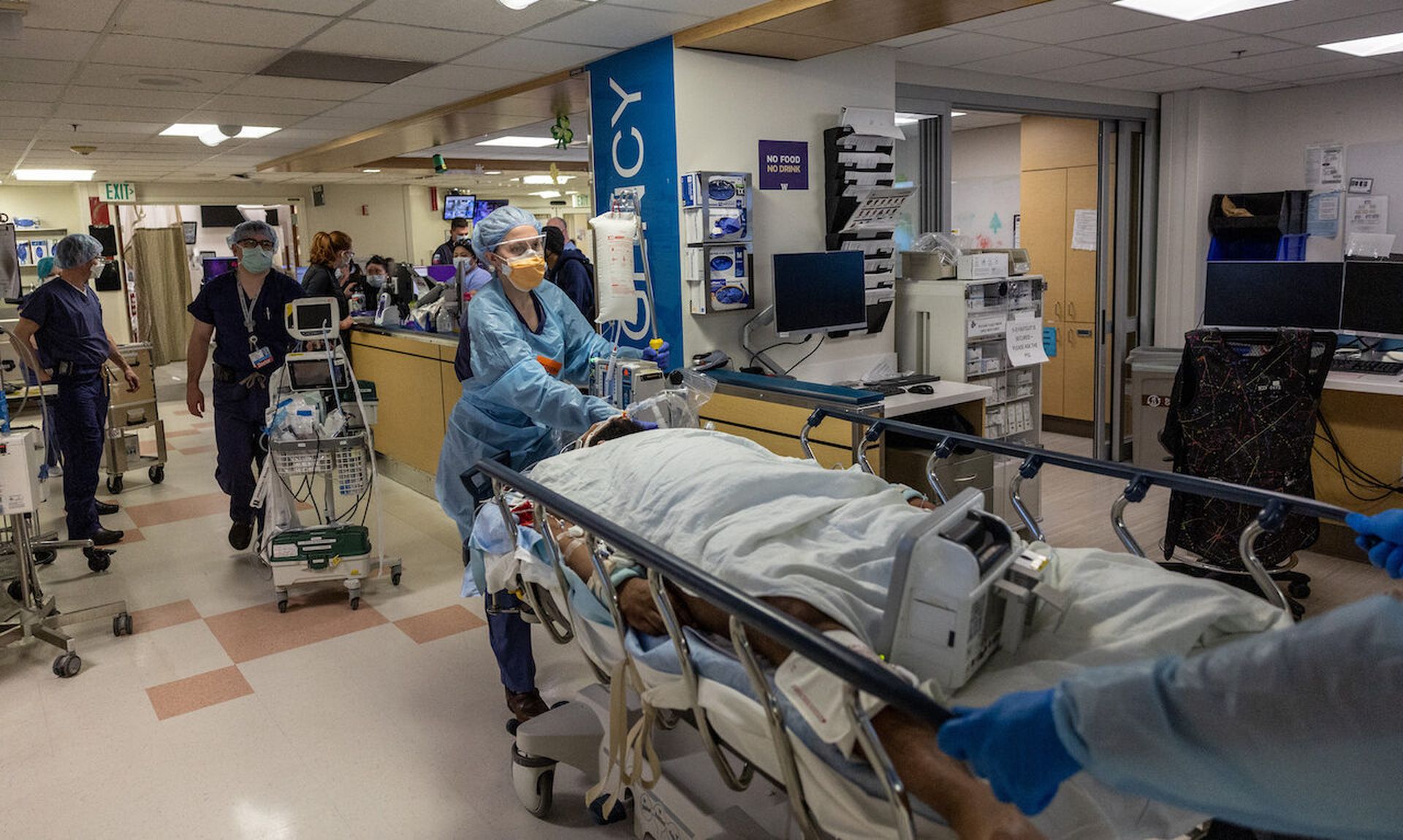
The government’s push for threat sharing and collaboration, with the uptick in alerts directed to the healthcare sector, are a welcomed shift in the longstanding efforts to curtail cybersecurity challenges with overall awareness and cyber posture in the industry.
But awareness doesn’t always translate into a viable solution, particularly when it comes to tackling the minutiae of medical devices. Due to the sheer complexity of the device ecosystem, resource constraints, and knowledge gaps, even the largest health systems struggle to solve the risk management challenges.
“I think medical devices and biomed in general… are really kind of the redheaded-stepchild of healthcare organizations because they're complex, and nobody really knows how to deal with them,” said Ben Denkers, CynergisTek’s chief innovation officer.
Consider the FBI alert on legacy medical devices, which resounded the bullhorn on risks associated with leveraging legacy tech in devices directly tied to patients. For many in healthcare, the messages rang familiar: groups like CHIME have long-warned of patch management issues and the impossibility of a real-time inventory in the healthcare environment. Similarly, the recommendations were rather vanilla: basic blocking and tackling at the end of the day.
Certainly, such reminders do no harm – encouraging some healthcare entities to leverage technology as a safeguard to defend against a specific threat or to reduce overall risk. But some argue that the challenges facing many providers can’t be boiled down into a singular problem or solution, and that the current assessment of risk could leave a vulnerable market unable to see the forest through the trees.
SC Media spoke to Denkers about this quandary, and how the market can better address multiple and sometimes conflicting hurdles to cybersecurity.
Persistent knowledge, staffing gaps
When the onslaught of ransomware attacks against healthcare began in 2016, the rallying cry was that there was no silver bullet to solve cybersecurity challenges. The sentiment remains, for both overall infrastructure and device security vulnerabilities.
As it’s likely always been in healthcare, the crux of its issues is actually a combination of resource and knowledge constraints, which are needed to truly have an effective security and privacy program, Denkers explained. Providers need a combination of people, processes, and technology to have a successful privacy and security program, even before it’s applied to a specific area like medical devices.
“If you don't have enough resources, it's going to be problematic. If you don't have the right technology, you're going to have issues. And if you don't have the right processes to make sure all of those are working and effective, it doesn't do you any good,” said Denkers.
“That's the problem. It's not a singular issue of, ‘hey, we don't have the right technology to stop the attack,’” he continued. “Let's say, magically, you can wave your wand and put in some sort of endpoint protection on all the medical devices. Great. But what happens if you don't have the people to monitor the alerts or have to deal with a device being compromised? It doesn't really do you any good.”
That means that even when a problem is identified, it still can’t be remediated without the effective processes or controls. And if the problem persists, it can create downstream effects when the device remains in use, which could still cause patient safety impacts.
Further, if hospital leadership doesn’t know how to use the actual security technology, “it’s not going to do a whole lot,” said Denkers. Others are struggling without the resources to manage or monitor the tools, or even tweak them to make it effective in the environment.
“I've had countless conversations with individuals at healthcare organizations, and similarly where they've invested a lot of money in technology for it to sit in the corner because they don't have the resources or the know-how, or the physical resources to take the device and implement it,” he added.
“And they certainly don't have the resources to validate that it's working. Medical device security is important, it absolutely is. But you're also talking to organizations that probably, I would venture to guess, don't even have endpoint protection.”
Some resource issues are financially driven; organizations don’t have the money to make investments in the technology stack, or afford to hire the right people. Hiring challenges also persist for rural providers, who may not be able to physically get people into the organization.
“Many rural hospitals face staffing challenges based on location alone,” he said. Healthcare is facing all of these problems, not just with medical devices and the higher level of risk due to the direct attachment to care. But “if you really start to unpeel the layers, you'll start to see that healthcare in general still isn't isn't necessarily the poster child for security and privacy programs.”
The elephant in the room
Denkers posed an important question: if a car manufacturer had vehicles on the road that generally did what they were supposed to do, but passengers were at risk due to a faulty airbag, or malfunctioning brakes, what would happen? The manufacturer would be forced to make changes.
“The reason why we're having to deal with these problems is because [medical devices] weren't properly developed from the beginning,” he mused. “It all starts with the software development life cycle, and where does SDLC start? It's whoever is developing the product or the solution.”
If issues aren't properly vetted at the beginning of the development cycle, risks emerge. As Denkers sees it, “it's the responsibility of the vendor to have a better product.”
It's a snowball effect: you're never really actually going to catch up because it's just going to continue to get worse and worse and worse every time you have outdated software or end-of-life hardware and products.
“It's interesting, those types of risks wouldn't be accepted in any other organization. But for some reason, we're dealing with people, which arguably have the highest rates of consequences, and it's okay,” said Denkers.
Addressing gaps, while threats increase
The FBI alert was likely intended to reflect the current threats facing vulnerable platforms, warning that bad actors are increasingly using unpatched medical devices to gain a foothold on the network.
But the alert should instead serve as a guidepost: An exploit could ultimately impact the integrity and confidentiality of data, or even worse, cause disruptions in operational functions and impact patient safety.
Use this “as a compass or a North Star,” Denkers recommended, and review the guidance to verify just how well medical devices are being protected. Many in healthcare are in situations where they think they have certain safeguards in place, or some version of recommended safeguards, inadvertently miss the most important element amid the noise.
As Denkers plainly puts it, “The question then really becomes: How effective is that control?”
An entity may have endpoint protection or access controls, but be unaware of potential gaps in the environment, or unclear whether tools adequately address vulnerabilities. Some “organizations generally don't have a mechanism in place to validate how effective controls are – whether it be people, processes, or technology,” he explained.
Segmentation is one of those areas where an entity might decide to separate certain devices from the main network, but then management of those devices is handled by another department. They set security and forget it. But as noted by Denkers, “if they're connected to the network, they're still connected to patients.”
And such oversights bring grave consequences. If a device or supporting infrastructure were to be compromised, and the device needs the internet to function or access certain portions of the environment, the medical devices can’t function for patient care.
Depending on the organization's requirements, there can be “many downstream effects from general compromises on the IT environment that become problematic quickly.”