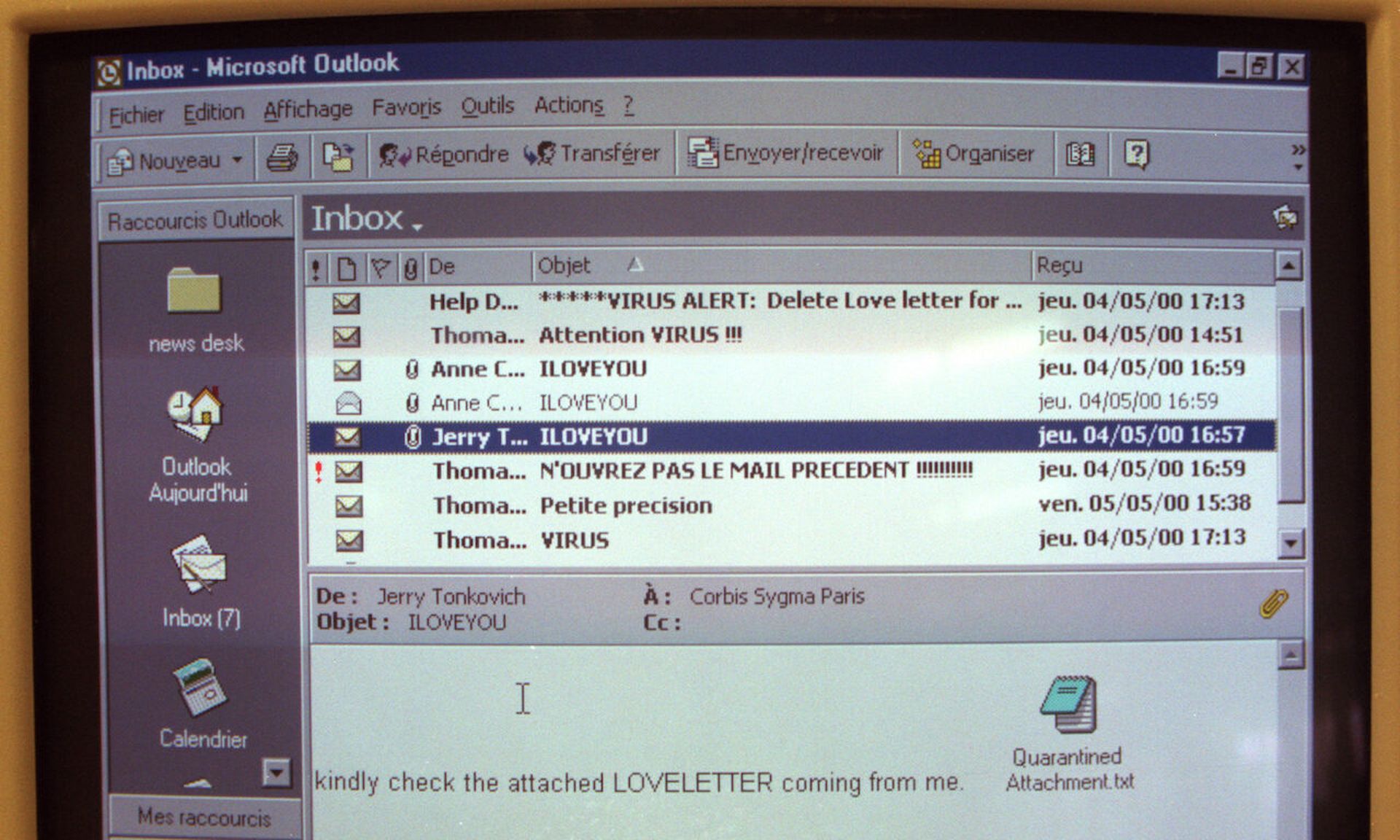
Twenty-three years ago, the digital world witnessed a cyberattack that would forever change our approach to cybersecurity. On May 5, 2000, the ILOVEYOU worm, also known as the Love Bug or Love Letter For You, infected more than 10 million Windows personal computers within days.
Major enterprises such as Ford Motor Company, AT&T, and Microsoft, as well as government organizations like the Pentagon, CIA, U.S. Army, and parliaments in Denmark and the U.K., had to shut down their email services to contain the damage. With an estimated 10% of internet-connected computers worldwide affected, the total damage could have exceeded $10 billion.
The seemingly innocent "love letter" email attachment proved irresistible to many, showing just how susceptible humans are to social engineering tactics. Despite technological advancements, the human brain remains the one vulnerability that's still the most difficult to fix.
In the digital age, we often focus on the technological aspects of cybersecurity. Yet, it’s the human factor that remains the weakest link in the chain. As we witness the rise of large language models such as ChatGPT and deepfake technologies, the potential for social engineering attacks at an unimaginable scale becomes an even more alarming problem.
As we venture further into the world of artificial intelligence, large language models like ChatGPT have the potential to revolutionize many aspects of our lives. However, this technology also poses a significant risk. AI-generated text, combined with deepfake technologies, can create convincing social engineering attacks on an unprecedented scale.
Threat actors can tailor-make these attacks to target individuals or organizations, exploiting the human tendency to trust and engage with familiar content. Experts predict the risk of these attacks will soon reach unprecedented heights with the increased use of deepfake technology. Attackers can now create incredibly realistic images, audio, and video to bolster their malicious campaigns, posing a significant challenge for individuals to distinguish between reality and deception.
Given the ever-evolving threat landscape, it’s crucial to educate ourselves and others about the importance of cybersecurity and the potential risks of social engineering. By understanding these tactics, we can better identify and defend against them.
Organizations must prioritize comprehensive cybersecurity training for their employees, with a strong emphasis on the human aspect of security. It's essential to raise awareness about the increasing risk of extremely convincing, highly-personalized scam messages that can easily trick even the most tech-savvy individuals. With the advancement of technology, we must remain vigilant and cautious when interacting with digital content, particularly unsolicited emails, attachments, or messages from unknown sources. As we enter an age where hackers can convincingly fake voices and even video messages, it's critical that we educate our employees, parents, and loved ones about the possibility of scam messages, including those that may appear to come from familiar people.
In addition to organizations, software vendors have a responsibility to prioritize the addition of usability and technological features to enhance security for their users. This includes the incorporation of end-to-end authentication measures for messages to prevent unauthorized access and reduce the risk of phishing attacks. Vendors should also implement features that warn users of suspicious or potentially fake content, especially those that appear to come from familiar sources. By focusing on these critical guardrails, software vendors can help create a safer digital environment for their users, establish trust, and protect their reputation in the market.
The ILOVEYOU worm serves as a poignant reminder that no matter how advanced our security measures become, security pros will always find the human factor the most challenging to address. As we continue to navigate the digital age and confront new threats posed by AI and deepfake technologies, we must remember the lessons learned from this simple, yet devastatingly effective cyberattack and strive to strengthen our "human firewall" to protect ourselves and our digital lives.
Aron Brand, chief technology officer, CTERA